Cloud Foundry – Architecture

Architecture Overview
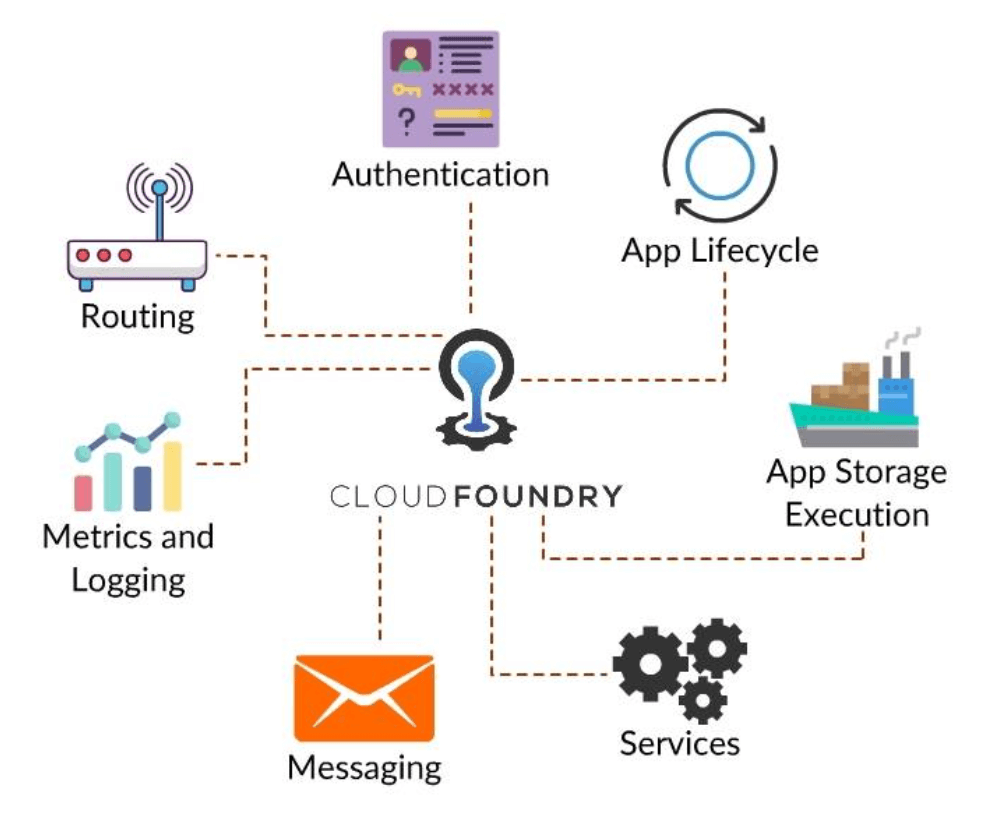

Routing & Authentication
-
Routerdirects the incoming traffic into the Cloud Foundry to the suitable component depending on whether it is a hosted application running on a Diego Cell or a Cloud Controller component. -
OAuth2 server (UAA)andLogin Serverwork together to provide identity management.

App Lifecycle
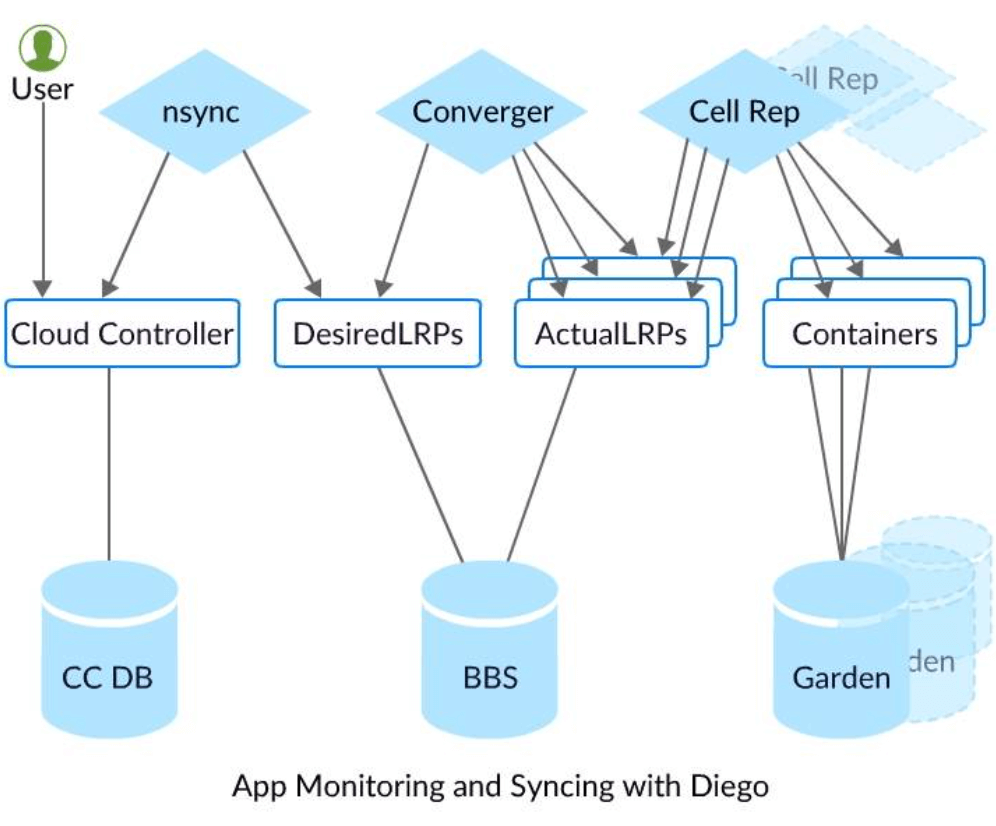
The following points explain the process of Cloud Foundry App Lifecycle.
-
-
An application deployments are directed by Cloud Controller. You target Cloud controller to push an app to Cloud Foundry.
-
nsync is responsible for writing the number of instances into a DesiredLRP structure in the Diego BBS database.
-
BBS monitors the DesiredLRP and ActualLRP values and ensures that their count match.
-
The containers are monitored by Cell Reps and provides the ActualLRP value.
-

App Storage & Execution
-
Blobstore– Repository for the large binary files that contain application code packages, Buildpacks, and Droplets. It can be configured either as an internal server or an external server. -
Diego Cell– Performs start and stop actions of an application locally in application virtual machine (VM), reports the app status and manages the VM’s containers. -
Garden– Makes the container technology available for the Diego project.

Services, Metrics & Logging
-
Service broker– Provides the service instance to an application that is provisioned and attached with a service by a developer. -
Metrics Collector– Gathers statistics and metrics from the components that are used to monitor a Cloud Foundry deployment by the Operators. -
App Log Aggregator– Streams application logs to developer.

Messaging
-
Bulletin Board System (BBS)– Stores more frequently updated and disposable data like the status of an application, heartbeat messages, and unallocated work. -
Consul– Stores longer-lived control data like component IP addresses and distributed locks. -
NATS– Broadcast the latest routing tables to the routers.

Quiz Time ?
Cool Stuff Below !


1



